Importance of Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is not just an option; it's a necessity for small businesses. The consequences of a cyber attack can be devastating, resulting in financial losses, reputational damage, and legal implications. By investing in robust cybersecurity measures, you can safeguard your business against these risks and gain the trust of your customers.
Moreover, with the rising number of cyber threats, many industries now require their partners and vendors to have adequate cybersecurity measures in place. By prioritizing cybersecurity, you can meet these compliance requirements and open doors to new business opportunities.
Understanding the Cybersecurity Landscape
To effectively navigate the digital landscape, it's crucial to have a solid understanding of the cybersecurity landscape. Stay updated with the latest cybersecurity trends, threats, and vulnerabilities. Subscribe to industry blogs, attend webinars, and participate in cybersecurity forums to stay informed. By having a clear picture of the potential risks your small business may face, you can proactively implement appropriate security measures.
Assessing Your Small Business's Cybersecurity Needs
Every small business has unique cybersecurity needs. Conduct a thorough assessment of your digital infrastructure to identify potential vulnerabilities. Consider factors such as the sensitivity of your data, the number of employees, and the types of devices used. This assessment will help you determine the areas where you need to focus your cybersecurity efforts.
1) Building a Strong Cybersecurity Foundation
2) Choosing the Right Cybersecurity Tools
3) Creating an Incident Response Plan
4) Compliance and Legal Considerations
5) Cybersecurity Best Practices for Remote Work
6) Staying Informed and Adapting
1) Building a Strong Cybersecurity Foundation

a) Password Policies and Access Controls
Implementing strong password policies and access controls is fundamental to protecting your small business from unauthorized access. Encourage employees to create complex passwords and regularly update them. Enforce multi-factor authentication for accessing sensitive systems or data. Limit access privileges based on job roles to prevent unauthorized access.
b) Software and System Updates
Regularly updating your software and systems is crucial for maintaining a secure digital environment. Cybercriminals often exploit vulnerabilities in outdated software to gain unauthorized access. Enable automatic updates whenever possible and regularly check for new patches and security updates.
However, it's important to be careful with the CMS (Content Management System) software updates. While updates often include essential security fixes, occasionally, they may cause compatibility issues or other unexpected problems. For instance, the last WordPress security update, featuring multiple security fixes, caused some sites to stop functioning.
Therefore, it's advisable to perform updates cautiously, especially for critical systems, and consider testing updates on a staging environment before applying them to your production site.
c) Employee Cybersecurity Training
Employees are often the weakest link in the cybersecurity chain. Conduct regular cybersecurity training sessions to educate your employees about common threats such as phishing, social engineering, and malware. Teach them how to identify suspicious emails, avoid clicking on unknown links, and report any security incidents promptly.
2) Choosing the Right Cybersecurity Tools
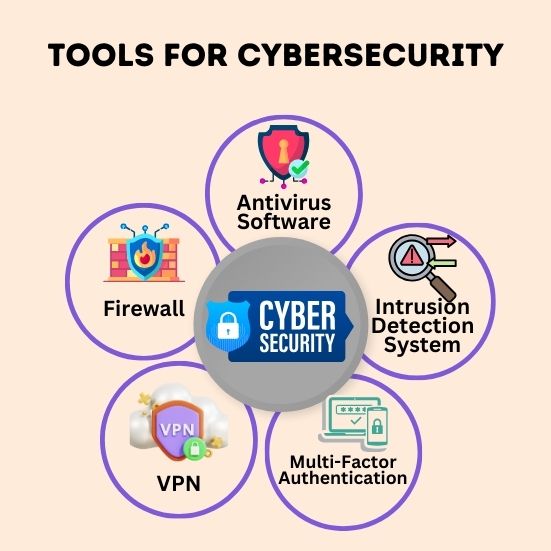
a) Antivirus Software and Firewall
Invest in reliable antivirus software and firewall solutions to protect your small business from malware and unauthorized access. These tools act as the first line of defense, scanning incoming and outgoing data for potential threats. Ensure that your antivirus software is regularly updated to detect the latest malware strains.
b) Intrusion Detection System (IDS)
An Intrusion Detection System (IDS) monitors network traffic for suspicious activities and alerts you in real-time. This proactive approach can help you detect and mitigate potential security breaches before they cause significant damage.
c) Cloud Security and Data Backup
If your small business leverages cloud services, ensure that the provider offers robust security measures, such as encryption and access controls. Additionally, implement a regular data backup strategy to protect your critical business data from loss or corruption. Cloud-based backup solutions can provide an extra layer of protection.
d) Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA):
MFA is a security tool that adds an additional layer of authentication beyond a username and password. Typically, it requires the user to provide two or more factors, such as something they know (password), something they have (a token or smartphone), or something they are (biometric data like fingerprints).
MFA enhances security by reducing the risk of unauthorized access, even if login credentials are compromised.
3) Creating an Incident Response Plan
Despite your best efforts, a cybersecurity incident may still occur. Having an incident response plan in place will help you minimize the impact and recover quickly. Define roles and responsibilities, establish communication channels, and outline the steps to be taken during a security incident. Regularly test and update your incident response plan to ensure its effectiveness.
4) Compliance and Legal Considerations
Depending on your industry, your small business may have specific compliance and legal requirements regarding cybersecurity. Ensure that you are aware of these regulations and take appropriate measures to comply with them. Failing to meet compliance standards can result in severe penalties and damage your reputation.
5) Cybersecurity Best Practices for Remote Work
With the rise of remote work, ensuring cybersecurity becomes even more critical. Implement secure remote access solutions, such as virtual private networks (VPNs), to protect data transmitted between remote employees and your business infrastructure.
Educate your employees about the risks associated with remote work and provide them with guidelines to follow, such as using secure Wi-Fi networks and locking their devices when not in use.
6) Staying Informed and Adapting
Cyber threats evolve rapidly, so it's crucial to stay informed about emerging trends and adapt your cybersecurity measures accordingly. Regularly review and update your security policies, conduct vulnerability assessments, and stay in touch with cybersecurity experts to ensure your small business remains protected against the latest threats.
Key Takeaways and Action Steps
To summarize, prioritizing cybersecurity is essential for the success and longevity of your small business. By understanding the cybersecurity landscape, assessing your specific needs, and implementing the recommended cybersecurity tips, you can safeguard your business from cyber threats. Remember to regularly review and update your security measures to stay ahead of potential risks.
Take action today by conducting a comprehensive cybersecurity assessment, educating your employees about cybersecurity best practices, and investing in robust cybersecurity tools and services. By doing so, you can protect your valuable data, maintain the trust of your customers, and secure the future of your small business.
Remember, cybersecurity is an ongoing process, so make it a priority and continuously adapt to new threats and technologies. Safeguarding your business from cyber threats is a never-ending journey, but with the right measures in place, you can navigate the digital landscape with confidence.










6 Essential Cybersecurity Tips for Small Businesses
Importance of Cybersecurity Cybersecurity is not just an option; it’s a necessity for small businesses....
Share this link via
Or copy link